Human Diseases Types, Causes, Solutions, and Preventive Measures for a Healthy Life
Diseases are an inevitable part of human life. They affect physical, mental, and social well-being, disrupting daily routines and reducing quality of life. Understanding the different types of diseases, their causes, solutions, and preventive measures is crucial to leading a healthy and fulfilling life. This article explores these aspects in detail.
Types of Diseases
Diseases can be broadly categorized based on their nature, origin, and duration. Below are the primary classifications:
Infectious Diseases:
These are caused by pathogens like bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. They spread through direct contact, contaminated food or water, insect bites, or airborne transmission.
Examples: Tuberculosis (TB), malaria, influenza, COVID-19, and HIV/AIDS.
Causes: Poor hygiene, lack of vaccination, contaminated environments, and weak immunity.

Non-Infectious Diseases:
These are not caused by pathogens and are not contagious. They are often chronic and result from genetic, environmental, or lifestyle factors.
Examples: Diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and asthma.
Causes: Sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, pollution, and hereditary factors.

Deficiency Diseases:
These result from the lack of essential nutrients in the diet.
Examples: Scurvy (Vitamin C deficiency), rickets (Vitamin D deficiency), and anemia (iron deficiency).
Causes: Poor dietary habits, malabsorption, and socioeconomic factors.

Genetic and Hereditary Diseases:
These arise due to genetic mutations and are often inherited.
Examples: Down syndrome, sickle cell anemia, and cystic fibrosis.
Causes: Mutations in DNA, inherited genes, and chromosomal abnormalities.
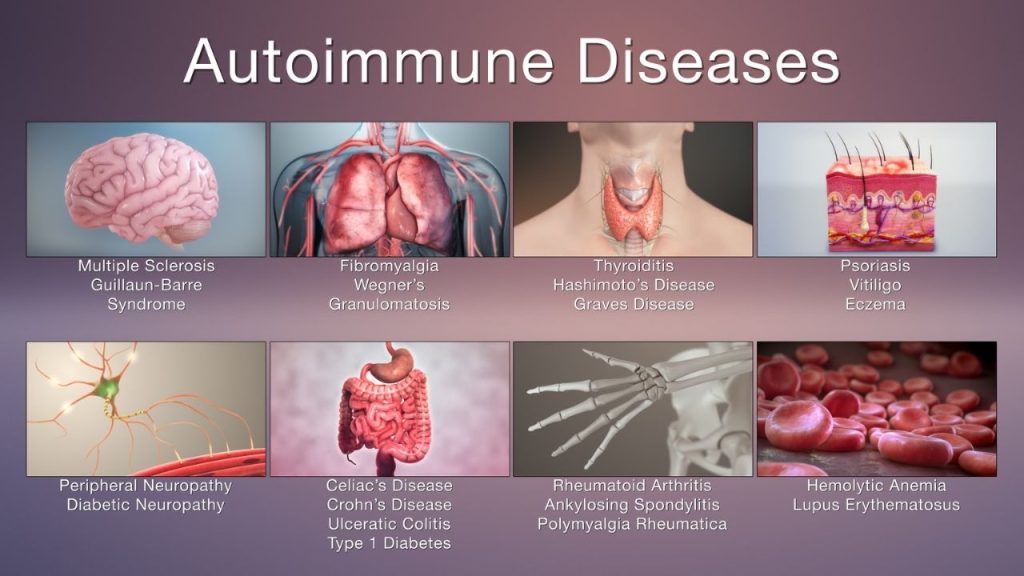
Autoimmune Diseases:
In these conditions, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy body cells.
Examples: Rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis.
Causes: Genetic predisposition, environmental triggers, and immune system dysfunction.
Mental Health Disorders:
These affect emotional and psychological well-being.
Examples: Depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia.
Causes: Stress, genetic factors, trauma, and chemical imbalances in the brain.
Lifestyle Diseases:
These are primarily caused by unhealthy habits and behaviors.
Examples: Obesity, hypertension, and Type 2 diabetes.
Causes: Poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption.
Common Causes of Diseases
While each disease has specific causes, several factors commonly contribute to disease development:
Poor Hygiene: Increases susceptibility to infections.
Unhealthy Diet: Deficiencies or excesses in nutrients affect overall health.
Lack of Exercise: Leads to obesity, cardiovascular issues, and weakened immunity.
Environmental Pollution: Triggers respiratory diseases and other health problems.
Stress: Weakens the immune system and exacerbates mental health disorders.
Genetics: Plays a significant role in hereditary and autoimmune diseases.
Age: Older age often brings reduced immunity and higher vulnerability.
Solutions and Treatments for Diseases
Medical Interventions:
Medications: Antibiotics for bacterial infections, antivirals for viral infections, and specific drugs for chronic diseases like diabetes and hypertension.
Vaccinations: Prevent diseases like polio, measles, and influenza.
Surgery: Required for conditions like cancer, heart diseases, and certain injuries.
Nutritional Therapy:
Addressing deficiencies with supplements (e.g., iron for anemia, Vitamin D for rickets).
Following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Regular exercise improves cardiovascular health, reduces obesity, and strengthens immunity. Avoiding tobacco, alcohol, and drugs prevents lifestyle-related diseases.
Psychological Support:
Counseling and therapy for mental health conditions like depression and anxiety. Medications for chemical imbalances and severe mental health issues.
Alternative Therapies:
Yoga, meditation, and acupuncture for stress management and holistic healing. Ayurveda and herbal medicine for managing chronic conditions.
Preventive Measures to Stay Fit and Healthy
Prevention is always better than cure. Adopting the following habits can significantly reduce the risk of diseases:
Prevention First:
The best treatment is prevention. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and stress management form the foundation of good health. Think of it as regular maintenance for your body – just like you wouldn’t wait for your car to break down before changing the oil.
Maintain Hygiene:
Wash hands regularly with soap and water. Ensure clean drinking water and proper sanitation. Regularly clean and disinfect living spaces.
Eat a Balanced Diet:
Include all food groups in appropriate proportions. Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive salt or fat intake.
Exercise Regularly:
Engage in moderate physical activity for at least 150 minutes a week. Include strength training and flexibility exercises. Click here
Regular Health Checkups:
Early detection through regular screening for conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and cancer. Monitor vital health parameters like blood pressure, sugar levels, and cholesterol.
Manage Stress:
Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing and mindfulness. Maintain work-life balance and prioritize mental health.
Avoid Harmful Substances:
Say no to smoking, drugs, and excessive alcohol. Limit exposure to pollutants and harmful chemicals.
Vaccination and Immunization:
Stay up to date with recommended vaccinations for children and adults. Take seasonal flu shots and other preventive measures as advised.
Prioritize Physical Health:
Engage in regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and adequate sleep. Avoid risky behaviors like unprotected sex and reckless driving.
Focus on Mental Well-being:
Seek help for mental health issues without stigma. Build strong social connections and practice gratitude.
Embrace Preventive Care:
Invest in health insurance and regular medical checkups. Follow public health guidelines during pandemics and outbreaks.
Stay Informed:
Medical knowledge continues to evolve. Staying informed about health issues and treatment options helps you make better decisions about your health care. Educate yourself about common diseases and their symptoms. Understand genetic predispositions and take proactive steps.
Early Detection:
Regular check-ups and screening tests can catch problems early when they’re most treatable. Don’t wait for symptoms to become severe before seeking medical attention.
Holistic Approach: Living a Disease-Free Life
Health isn’t just about treating symptoms – it’s about addressing the whole person. Physical health, mental well-being, social connections, and environmental factors all play crucial roles in disease prevention and treatment. Achieving a disease-free life requires a holistic approach encompassing physical, mental, and emotional health.
Personal Responsibility:
While medical professionals play a vital role in treating disease, each person must take responsibility for their health through lifestyle choices and adherence to treatment plans.
The Future of Disease Management
We’re entering an exciting era in medicine. Advances in genetics, artificial intelligence, and biotechnology are opening new frontiers in disease prevention and treatment. Personalized medicine, based on individual genetic profiles, promises more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
But even as technology advances, the basics remain crucial. No amount of medical technology can replace the fundamental needs of the human body: good nutrition, regular exercise, adequate rest, and stress management.
Remember, your body is remarkably resilient and has powerful self-healing capabilities. By understanding different types of diseases and taking appropriate preventive measures, you can significantly improve your chances of maintaining good health throughout your life.
The key is to view health not as the absence of disease, but as an active state that requires ongoing attention and care. Think of it as tending a garden – regular maintenance and care yield the best results, but it’s never too late to start making improvements.
Your body is the only place you have to live in. Treat it well, listen to its signals, and give it what it needs to thrive. After all, good health is not just about living longer – it’s about living better. Click here
Conclusion
Human diseases are diverse, ranging from infectious conditions to chronic lifestyle disorders. While many diseases have effective treatments, prevention remains the most powerful tool. By adopting healthy habits, staying vigilant about symptoms, and seeking timely medical care, individuals can significantly reduce their disease burden and enhance their quality of life. The journey to a healthier, disease-free life begins with small, consistent steps toward wellness and a proactive approach to health care.